Semantic SEO: Comprehensive Guide to Increasing Traffic and Sales.
Is your SEO strategy keeping up with the evolution of search engines? In a digital world where every second brings new data and changing algorithms, relying solely on traditional search engine optimization (SEO) methods can be insufficient. For years, SEO was synonymous with keywords – their density, placement, and count. The goal was to stuff content with relevant phrases to make a search engine deem it relevant. However, those days are over. Today, to effectively compete for the attention of users and algorithms, we must look much broader.
The future, and in fact the present, belongs to Semantic SEO. This is an approach that goes beyond simple keyword matching, focusing on understanding user intent and the context of the content. Search engines, powered by advanced artificial intelligence, not only index words but also try to understand the meaning behind a query and provide the most comprehensive and valuable answer. This is a paradigm shift that requires us, SEO specialists and content creators, to adopt a completely new way of thinking.
The goal of this comprehensive guide is not only to explain what semantic SEO is but, above all, to show how to implement it in practice. You will learn how to use its potential to increase organictraffic, improve visibility in search results, and, most importantly, translate this into real sales and the growth of your business. Get ready for a journey into the future of SEO, which is already here and now.
The Evolution of SEO: From Keywords to Intent and Context.
Before diving into the intricacies of semantic SEO, it’s worth understanding where we came from. For a long time, search engine optimization was a relatively simple task. It focused on traditional SEO, which relied primarily on keyword matching. Website creators tried to include target phrases as many times as possible in the content, headings, and even metadata. Unfortunately, this often led to practices like keyword stuffing – unnaturally cramming keywords, which negatively affected the readability and quality of the text for the user. Search engines, being less advanced than today, were susceptible to such manipulations, allowing for high rankings even for low-quality content.
However, with the development of technology and growing user expectations, search engines began to evolve. They realized that simply matching keywords was not enough. Users no longer just type in single phrases; they ask questions, seek solutions to problems, and compare products. In response to these needs, semantic search was born. This is an approach where the search engine not only analyzes keywords but, above all, tries to understand the context of the query and the user’s intent. The goal is to provide the most relevant and comprehensive results, even if the words used are not identical to those in the content.
Interesting Fact: The origins of semantic search date back to the concept of LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing), which appeared as early as the 1980s. LSI assumed that words that frequently appear together in a text are semantically related. Although Google never confirmed the direct use of LSI as a ranking algorithm, the idea behind it – understanding the relationships between words and concepts – became the foundation for later, much more advanced algorithms.
Google’s algorithms have played a crucial role in this evolution. They are the brains behind understanding natural language and context. Here are some of the most important ones that revolutionized SEO:
RankBrain. Introduced in 2015, it was one of Google’s first AI-powered algorithms. Its main task was to interpret complex and unfamiliar queries. RankBrain could understand the intent behind a query, even if it had never seen it before, which was a breakthrough in handling so-called “long-tail keywords” and unique phrases. Thanks to it, the search engine began to better understand what the user truly wanted to find, not just what they typed.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers). Launched in 2019, BERT was another giant leap towards understanding the nuances of natural language. Unlike previous algorithms that analyzed words in isolation or in simple sequences, BERT can analyze words in the context of an entire sentence, both before and after a given word. This allowed Google to much better understand queries, especially those with prepositions and complex constructions that could previously be misinterpreted. For example, the difference between “Python programming course” and “Python in a programming course” became clear to the search engine.
MUM (Multitask Unified Model).Introduced in 2021, MUM is the future of search, and its capabilities are truly impressive. It is a multimodal algorithm, meaning it can understand information in various formats – text, images, video, audio – and combine them. Moreover, MUM is capable of answering complex questions that require synthesizing information from multiple sources and languages.
For example, if you ask, “Can I use the same bike for commuting and mountain trails, and how does that compare to my current road bike?”, MUM will be able to understand all aspects of the query and provide a comprehensive answer, even if it requires translation and analysis of data from different languages. This means an end to the need for multiple queries to find an answer to a complex problem.
Why is this evolution so important for your business? Because it signifies the definitive end of “keyword stuffing” and algorithm manipulation. Search engines are now too intelligent to be fooled. Instead, the era of “topic authority” has begun – building authority in a given field by creating comprehensive, valuable, and contextually rich content. Companies that understand and implement semantic SEO will not only be able to reach a wider audience but also build lasting relationships with users by providing them exactly what they are looking for, when they need it.
Foundations of Semantic SEO: Intent, Entities, and Knowledge Graphs.
Understanding the evolution of search engines is the first step. The second, and perhaps most important, is delving into the foundations of semantic SEO: user intent, entities, and knowledge graphs. These elements form the core of how modern search engines understand the world and deliver relevant results.
User Intent: The Key to Success in Semantic SEO.
Forget what the user types into the search bar. Focus on why they are typing it. This is user intent – the goal behind every query. Search engines, like Google, are becoming increasingly better at guessing this intent, and your task is to create content that perfectly matches it. Understanding intent is absolutely crucial for success in semantic SEO, as it determines whether your content will be considered valuable and appear in search results.
We distinguish four main types of intent:
Informational Intent. The user is looking for information, answers to a question, or wants to learn something. Query examples: “how to bake bread,” “history of Rome,” “what is semantic SEO.” Content matching this intent includes blog articles, guides, encyclopedias.
Navigational Intent. The user wants to reach a specific website or location. Query examples: “Facebook login,” “Google homepage,” “Company X contact.” Content matching this intent includes homepages, contact pages, social media profiles.
Transactional Intent. The user is ready to make a purchase or another conversion. Query examples: “buy Samsung Galaxy S24 smartphone,” “cheap flights to Barcelona,” “car insurance online.” Content matching this intent includes product pages, shopping carts, booking forms.
Commercial Investigation Intent. The user is researching the market, comparing products or services before making a purchase decision. Query examples: “best gaming laptop 2025,” “iPhone 16 vs. Samsung Galaxy S25 reviews,” “mortgage comparison.” Content matching this intent includes reviews, comparisons, rankings, buying guides.
How to identify intent and create content that matches it?
✅ Analyze queries: Instead of just looking at keywords, consider what the user wants to achieve by typing a given phrase. Are they looking for a quick answer, do they want to buy a product, or are they comparing options?
✅ Check SERP (Search Engine Results Page): Google search results are the best indicator of intent. If informational articles dominate for a given query, it indicates informational intent. If product pages and price comparison sites appear, the intent is transactional or commercial.
✅ Create comprehensive content: For informational intent, create an article that exhausts the topic. For transactional intent, ensure the product page contains all necessary information, photos, and reviews.
Entities: What They Are and Why They Are More Important Than Keywords.
In the era of semantic SEO, entities have become the new “keywords,” though they are much more complex. An entity is any unique, well-defined thing or concept about which Google can gather information and build relationships. It can be a person (e.g., “Albert Einstein”), place (e.g., “Paris”), object (e.g., “iPhone”), organization (e.g., “NASA”), event (e.g., “Olympics”), or abstract concept (e.g., “democracy”).
Google uses entities to build relationships and understand the world. Instead of treating words as isolated character strings, the search engine sees them as parts of a larger network of connections. For example, when you search for “Eiffel Tower,” Google doesn’t just see these two words but understands that “Eiffel Tower” is an entity that is a structure, located in Paris, designed by Gustave Eiffel, and is a symbol of France. All this information is interconnected.
Fun fact: The role of entities in personalizing search results is enormous. Google, understanding entities, can tailor results to your location, search history, and preferences. If you often search for football information and then type “Lewandowski,” Google is more likely to show you results about Robert Lewandowski rather than another person with the same surname.
To see how entities can supercharge your content strategy, check out this guide on entity-based SEO in NEURONwriter.
Knowledge Graph: Visualizing Google’s Understanding of the World.
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a powerful database that collects and organizes information about billions of entities and their relationships. It can be imagined as a giant network where nodes are entities and edges are the relationships between them. It is thanks to the Knowledge Graph that Google can provide direct answers to questions, display Knowledge Panels on the right side of search results, and generate Rich Snippets.
How does the Knowledge Graph work and where does it get its data? Google collects data from many sources, including Wikipedia, the CIA World Factbook, Freebase (whose data has been incorporated into the Knowledge Graph), as well as its own algorithms that analyze content on the internet. It systematizes this information, creating a coherent picture of the world.
Fact:Google’s Knowledge Graph contains billions of facts and relationships, making it one of the largest collections of organized knowledge in the world.
How can your business appear in the Knowledge Graph?
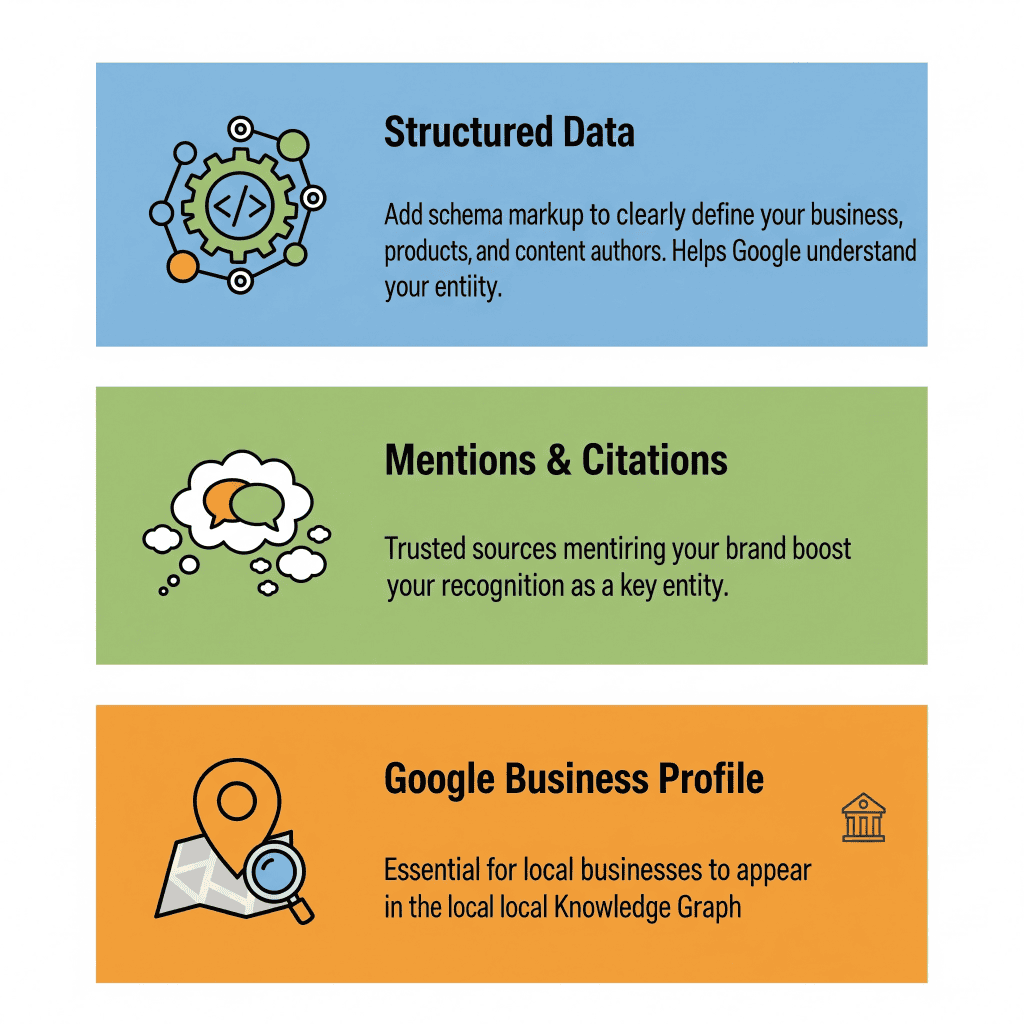
Understanding intent, entities, and the Knowledge Graph is the foundation for building an effective semantic SEO strategy. It’s a shift from thinking about individual words to thinking about entire concepts and relationships, which allows for the creation of content that is not only visible but, above all, valuable and relevant to users.
Practical Strategies for Implementing Semantic SEO.
Having understood the theoretical foundations of semantic SEO, it’s time to move on to practicalities. How can you translate this knowledge into actionable steps that will increase traffic and sales? Here are the key strategies you should implement.
Keyword Analysis in the Semantic Era: From Words to Topics.
Traditional keyword analysis, while still important, must be supplemented with a semantic approach. We are no longer just looking for individual phrases, but entire topics and topic clusters that are related to user intent. The goal is to identify all aspects of a given topic that may interest your target audience.
How to do it?
1️⃣ Brainstorm around main topics: Instead of thinking about a “keyword,” think about a “topic.” If you run a coffee shop, topics might include “coffee beans,” “coffee brewing methods,” “history of coffee,” etc.
2️⃣ Analyze intent: For each topic, consider what intentions might lie behind user queries. Are they looking for information, or do they want to buy a specific type of coffee?
3️⃣ Use tools: Tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, Surfer SEO, or even the free Google Keyword Planner and Google Search Console, will help you discover related phrases, questions users ask, and popular topics in your niche. Pay attention to the “People also ask” and “Related searches” sections in Google – they are a treasure trove of content ideas.
4️⃣ Competitor analysis: Check what topics and topic clusters your competitors are covering and how they are organized. Look for gaps you can fill.
Creating Comprehensive and Authoritative Content: Topic Clusters.
The central element of semantic SEO is creating content that is not only optimized for keywords but, above all, comprehensive, valuable, and authoritative on a given topic. This is where Topic Clusters come into play.
Topic Clusters are a way of organizing content on a website that helps search engines understand your expertise in a given field. Instead of creating many individual articles on similar but not identical keywords, you create one comprehensive main article (the pillar page) and many smaller, detailed articles (the cluster pages) that expand on specific aspects of the main topic. All cluster pages link to the pillar page, and the pillar page links to the cluster pages, creating a cohesive network of connections.
Topic Cluster Model:
Pillar Page. A comprehensive, general article that covers a broad topic thoroughly but generally. It doesn’t have to answer all detailed questions but should serve as a starting point and contain links to more detailed content. Example: “The Complete Guide to Coffee Beans.”
Cluster Pages. Detailed articles that delve into specific aspects of the main topic. Each cluster page should answer specific questions or discuss narrower subtopics. Examples: “How to Brew Coffee with an Espresso Machine,” “Types of Coffee Beans: Arabica vs. Robusta,” “The History of Coffee in Europe.”
How to plan and structure clusters?
Choose a pillar topic. It should be broad but specific enough to build many subtopics around it.
Identify subtopics. These will be your cluster pages. Ensure each subtopic is comprehensive enough to warrant a separate article.
Create a link map. Plan how cluster pages will link to the pillar page and vice versa. Use natural, contextual links.
Content Depth and Breadth. In semantic SEO, it’s not just what you write, but also how deeply and broadly you cover a topic. Strive to address all aspects of a topic, anticipate user questions, and provide comprehensive information. Use natural language – write as if you were talking to an expert, avoiding repetition and unnatural phrasing. Remember, you are writing for people, not just algorithms.
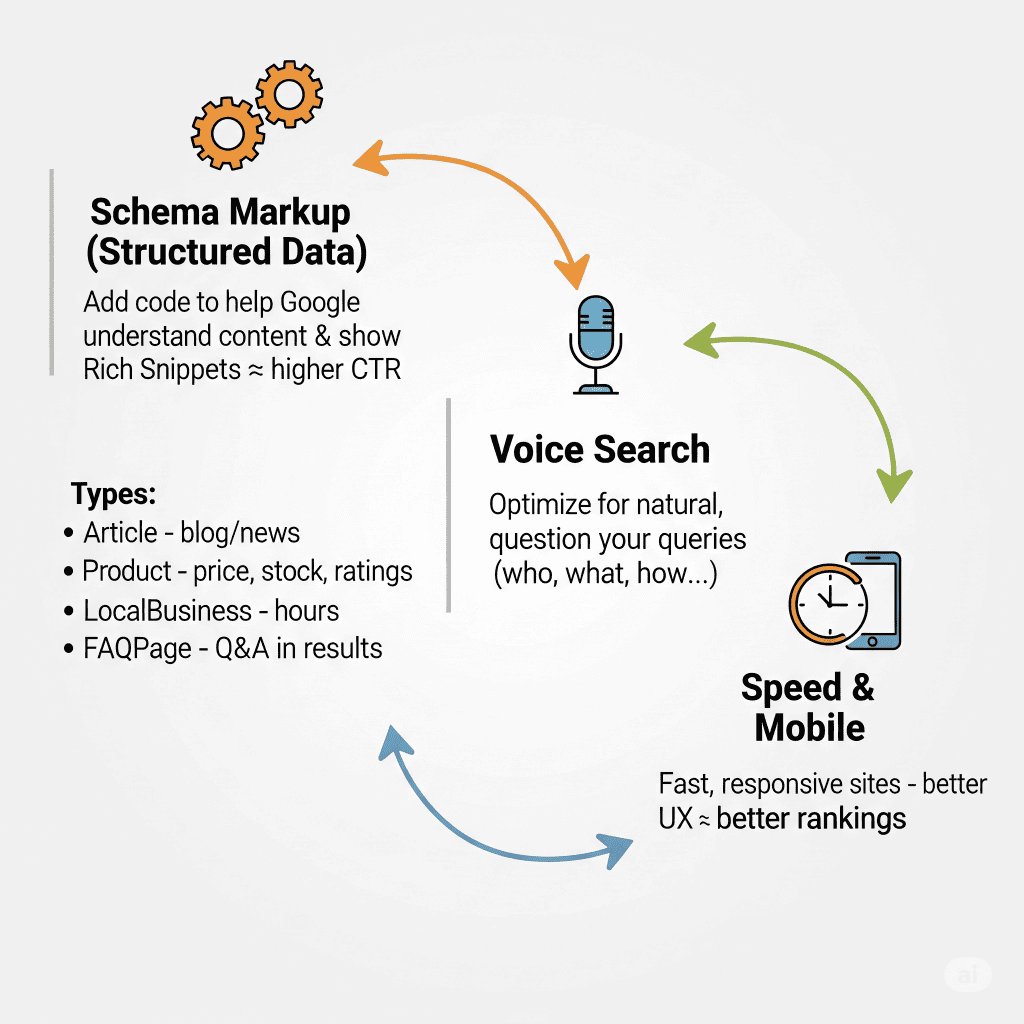
Technical Optimization for Semantics.
Although semantic SEO emphasizes content and context, technical optimization still plays a crucial role. It helps search engines better understand your site and its content.
Building Authority and Trust (E-E-A-T).
Google increasingly prioritizes content quality and trustworthiness. In this context, the concept of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) plays a key role. This is a set of guidelines Google uses to assess the quality of websites, especially for YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics, which can impact users’ health, finances, or safety.
Experience: Demonstrating that the content creator has direct, practical experience in the topic discussed. This is not just theoretical knowledge but the ability to apply it in practice. For example, a product review written by someone who has actually used it will have greater value
Expertise: Creating content by experts in a given field. Does the author have the appropriate qualifications, education, or experience to write on the topic? Are they recognized as an authority in their niche?
AuthoritativenessMeans that the site or author is recognized as an authority in a given field by other experts and credible sources. This is measured by links from other authoritative sites, media mentions, citations, and overall industry reputation.
Trustworthiness: The most important element. Is the site secure (HTTPS)? Is the information accurate and true? Is the company transparent (contact details, privacy policy)? Are reviews and opinions available? Trustworthiness builds confidence for both users and search engines.
Fact: E-E-A-Tis an increasingly important Google ranking factor, and its significance will only grow. Google wants to provide users with the most reliable and valuable information, and sites that demonstrate a high level of E-E-A-T have a better chance of ranking high in search results.
By implementing these practical strategies – from semantic keyword analysis, through creating topic clusters and technical optimization, to building E-E-A-T authority – you are building a solid foundation for your semantic SEO strategy. This is an investment that will bring long-term benefits in the form of increased traffic, better visibility, and, most importantly, more conversions.
Measuring Success and the Future of Semantic SEO.
Implementing semantic SEO is a long-term process that requires patience and continuous optimization. However, to know if your efforts are yielding the desired results, it is crucial to measure success and understand how the future of search will shape semantic SEO.
Success Metrics in Semantic SEO.
Traditional SEO metrics, such as ranking for individual keywords, are still important, but in a semantic context, we need to look broader. Here are key indicators to help you assess the effectiveness of your strategy:
Increased organic traffic for entire topics: Instead of focusing on traffic growth for a single phrase, analyze how traffic increases for entire topic clusters or broad queries related to your niche. Semantic SEO aims to attract users who are looking for information on a given topic, not just a specific keyword.
Improved rankings for complex queries and questions: Search engines are increasingly better at understanding complex queries and questions. Monitor whether your site appears high in rankings for long, conversational phrases that reflect user intent.
Increased conversions and sales: The ultimate goal of most SEO efforts is to increase revenue. Semantic SEO, by better matching content to user intent, should lead to a higher conversion rate and, consequently, to increased sales. Monitor which topics and content generate the most leads or transactions.
Appearance in Rich Snippets, Direct Answers, Knowledge Panel:These are clear signals that Google perfectly understands your content and considers it authoritative. Appearing in these featured search results significantly increases your site’s visibility and credibility.
Increased time on page and reduced bounce rate: If your content is comprehensive and answers user intent, they will spend more time on it and be less likely to return to search results. This is a positive signal for Google, indicating the high quality and relevance of your page.
The Future of Semantic SEO.
Semantic SEO is not a fleeting trend but the direction in which the entire search industry is heading. The future will bring further evolution of AI in search engines, meaning an even better understanding of natural language, context, and user intent. Algorithms will become increasingly sophisticated, and their ability to synthesize information from various sources will grow.
Personalization of search results: Search engines will increasingly tailor results to individual preferences, search history, and user location. This means that for the same query, two different people may see slightly different results, which emphasizes the importance of building topic authority and content comprehensiveness.
Increased importance of visual and multimodal search. With technological advancements, we will increasingly search for information using images, video, or voice. Algorithms like MUM already show that search engines will be able to process and understand information in various formats simultaneously. This means that optimizing images, videos, and other media will become even more important.
Interesting Fact: Semantic SEO is the best way to prepare your site for future algorithm changes. By focusing on delivering valuable, comprehensive, and contextually rich content, you build a foundation that will be resilient to subsequent Google updates. Search engines will always reward sites that best meet user needs and provide them with the most relevant information. This is an investment in long-term success, not short-term tricks.
Conclusion
Semantic SEO is much more than just another optimization technique – it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about content and its role on the internet. We have stopped optimizing for robots and started creating for people, considering their intent and context. Search engines, powered by increasingly advanced artificial intelligence, are no longer just keyword-matching machines; they have become intelligent assistants that understand the meaning, relationships, and nuances of natural language.
The key to long-term success in search engines is adopting a semantic approach. This means focusing on:
- Understanding user intent and creating content that comprehensively addresses it.
- Building topical authority through topic clusters and deep, valuable content.
- Utilizing entities and structured data to help search engines organize and present your information.
- Demonstrating E-E-A-T, which includes experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, building confidence for both users and Google.
Don’t wait for your competition to get ahead. Start optimizing for intent and context today. This is an investment that will not only increase your organic traffic and sales but also build lasting value for your brand in the digital world. The future of SEO is semantic, and you now have the tools to shape it.
We also encourage you to read our previous article on semantic SEO:What Most People Misunderstand About Semantic SEO: The Iceberg of Reality
